Deflection is the immediate sag produced when an object is set on a structural member.
Rafters and roof ridges are normally under deflection.
Duration of load is 1 15 snow tributary length 12 0 exclude outer 6 ft of rafters which bear on outside walls the ridge beam.
Supporting roof and floor.
All structural members will deflect or flex under load.
If the sagging appears in the plane of the roof that is up and down between the ridge and the eave and from side to side the sagging is probably due to deflection and creep of the rafters themselves figures 8 and 9.
Ridge beams are required by code if the roof slope is less than 3 in 12 irc section r802 3.
You have probably seen this and it is most likely due to roof deflection sag and creep.
Some of these can support the roof and prevent ridge sagging and wall spreading.
Allowable deflection is generally expressed as a fraction of the span in inches.
Typically for better performing floors minimal defection is desired.
Deflection criteria default deflection criteria for the following members.
Ridge beam single span.
Ridge beam sizing is based on the span of the beam between supports and the amount of roof load supported by the beam.
Deflection criteria for rafters roof beams joists and floor beams.
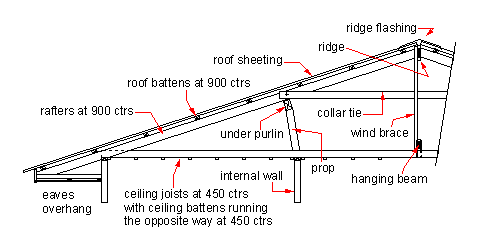
In homes with conventional ridges the rafters support the weight of the roof and transmit the roof load down through the walls to the foundation and finally to the soil.
Collar ties rafter ties tension beams structural ridge beams.
A ridge board is a non structural member that serves as a prop for opposing rafters to rest against and connect to.
The route taken by the weight of the roof through the framing members to the soil is called the load path.
Roof beam double span.
The amount of flex depends on the magnitude of the load applied span of the member and stiffness of the member.
Removal of the lateral bracing necessary for a roof rafters that are framed without a ridge beam will make the ridge dip noticeably as in the photo below.
Structural defects undersize roof rafters or trusses that have had their center web members removed to make room for attic storage can cause a roof to sag along its span.
This article describes and illustrates the different types of support that prevents roof sagging and wall bulging at buildings including definitions of collar ties rafter ties and structural ridge beams.
What you see is the result of weight and time and gravity.
The center beam is probably not terribly thick.